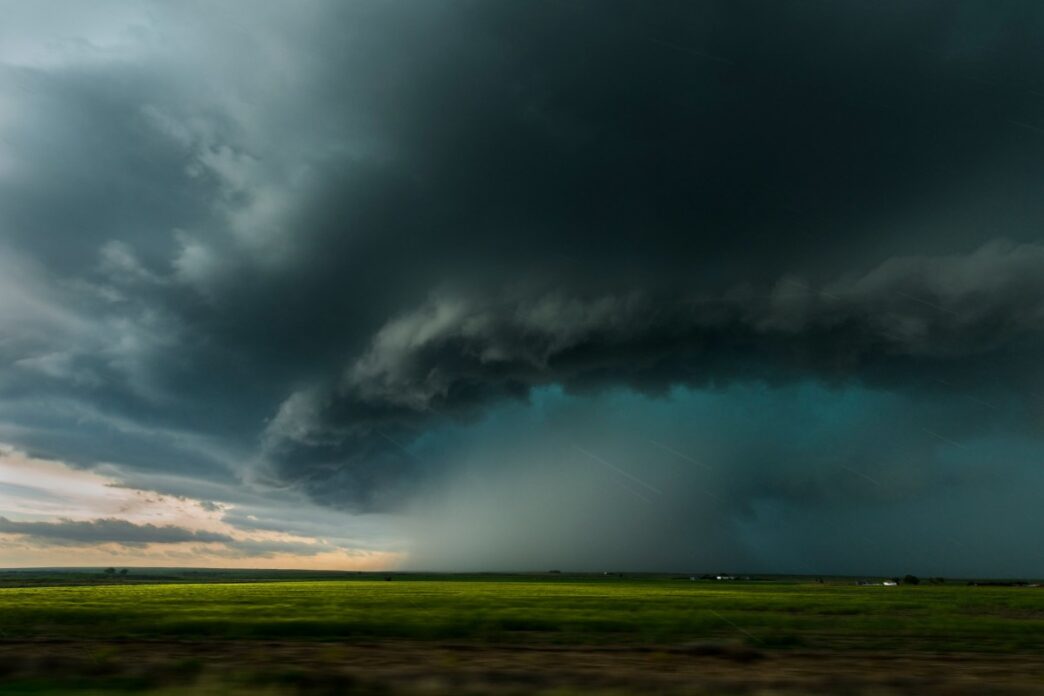
Rainmaker teams up with AI weather startup Atmo to boost cloud seeding precision.
The two firms exclusively told TechCrunch about their new partnership. Atmo will use deep learning models to spot clouds ripe for seeding. They’ll also push Rainmaker’s drone-based cloud seeding services to their customers.
On the flip side, Rainmaker will share radar data to measure how much rain their cloud seeding actually triggers.
This partnership hits amid crackdowns on conspiracy theories blaming Rainmaker for recent Texas floods—a claim scientists say is baseless.
Professor Bob Rauber of the University of Illinois broke down the scale issue to TechCrunch last week:
“Somebody is looking for somebody to blame.”
Though cloud seeding can nudge clouds to drop more precipitation, it’s a small amount compared with the size of a storm. One well-documented case in Idaho released an additional 186 million gallons of precipitation, which pales in comparison with the “trillions of gallons of water” a large storm will process.
Cloud seeding is common in the Western U.S. mainly to boost snowpack and reservoir levels. Texas uses it to coax extra rain during summer storms, but the results are modest.
The West Texas Weather Modification Association, a longtime Rainmaker partner, says cloud seeding has boosted precipitation around 15%, or two inches annually there.
Rauber noted the difference comes down to cloud types and geography:
Rainstorms are even less responsive, since they’re already primed to drop plenty of precipitation.
Rainmaker and Atmo are betting AI can help scale cloud seeding effectiveness by zeroing in on prime clouds and tracking real impact in real time.